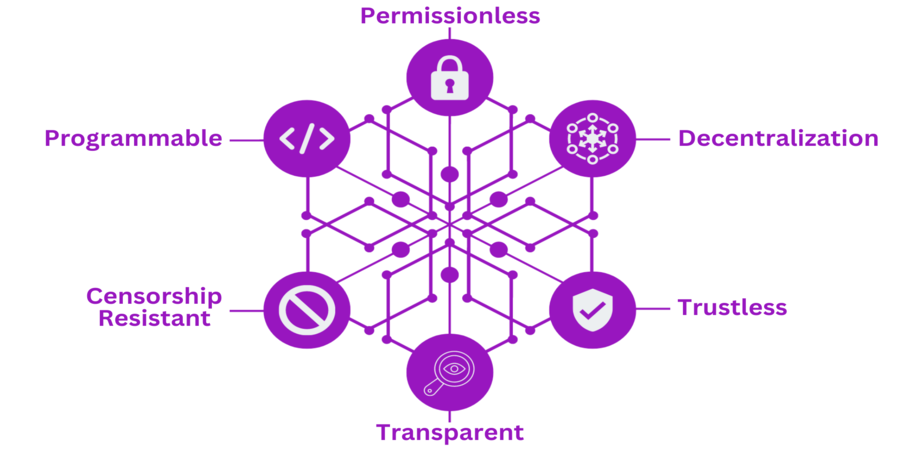

What is decentralized finance (DeFi)?
The term "decentralized finance" (or "DeFi") refers to a new movement in the financial sector. It has been gaining popularity over the past few years and has the potential to revolutionize the traditional financial system. DeFi is a decentralized network of financial applications built on a blockchain that operates without intermediaries, such as banks or other financial institutions. In this article, we will explore what DeFi is, how it works, and the potential benefits and risks of this emerging technology.
What is DeFi?
DeFi, as the name suggests, is a decentralized network of financial applications that operate on a blockchain. It is built on the same technology as cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but instead of being a currency, DeFi consists of a network of financial applications that operate on a decentralized platform. This means that there is no central authority or intermediary involved in the transactions, which reduces the risk of fraud and hacking.
How does DeFi work?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a network of financial applications that operate on a blockchain. It is built on the same technology as cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but instead of being a currency, DeFi consists of a network of financial applications that operate on a decentralized platform.
DeFi applications are built on smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts that are programmed to automatically execute certain actions when certain conditions are met. Smart contracts are a key component of DeFi because they allow for the automation of financial transactions without the need for intermediaries, such as banks or other financial institutions.
The financial services provided by DeFi apps span lending, borrowing, trading, and investing. Here are some examples of how some of the most common DeFi applications work:
- Lending: DeFi lending platforms allow users to borrow and lend funds without the need for a bank or other financial institution. Users can deposit their funds into a smart contract, which then lends the funds to borrowers at a predetermined interest rate. The interest earned by lenders is paid out automatically by the smart contract, and borrowers must provide collateral to secure their loans.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DeFi DEXs allow users to trade cryptocurrencies without the need for a centralized exchange. DEXs operate on a peer-to-peer basis, with buyers and sellers trading directly with each other. DEXs use smart contracts to execute trades and handle the exchange of funds.
- Stablecoins: Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies that are pegged to the value of a fiat currency, such as the US dollar, to provide stability and reduce volatility. DeFi stablecoins are typically backed by a reserve of the underlying currency, which is held in a smart contract. Users can exchange their cryptocurrencies for stablecoins on a DeFi platform, and then use the stablecoins for trading, investing, or other financial transactions.
- Yield Farming: Yield farming is a DeFi strategy that allows users to earn rewards by providing liquidity to a DeFi application. Users can deposit their funds into a liquidity pool, which is used to facilitate transactions on the platform. In exchange for providing liquidity, users earn rewards in the form of the platform's native tokens.
Benefits of DeFi
DeFi offers several potential benefits over the traditional financial system. One of the biggest advantages is that it eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks, which reduces costs and increases efficiency. The public ledger of all DeFi transactions allows for greater openness and transparency. This makes it easier to track and audit financial transactions, which can help reduce fraud and increase accountability.
Another potential benefit of DeFi is that it is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their location or financial status. This can help promote financial inclusion and give people who do not have access to traditional financial services a way to participate in the global economy.
Risks of DeFi
While Decentralized Finance (DeFi) offers several potential benefits over the traditional financial system, it also comes with some risks that users should be aware of. Here are some of the risks of using DeFi:
- Lack of Regulation and Oversight: One of the biggest risks of using DeFi is the lack of regulation and oversight. DeFi operates on a decentralized platform, which means that there is no central authority or intermediary to enforce security standards or protect user funds. This can lead to a higher risk of fraud and hacking, as there is no one to monitor or regulate the activities of the participants.
- Market Volatility: Another risk of using DeFi is market volatility. The value of cryptocurrencies, which are the basis of many DeFi applications, can be highly volatile and subject to sudden fluctuations. This means that users who invest in DeFi applications are at risk of losing their funds if the market experiences a downturn.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: DeFi applications are built on smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts that are programmed to automatically execute certain actions when certain conditions are met. If there is a flaw in the smart contract code, it can lead to unintended consequences, such as the loss of user funds. While smart contracts are designed to be secure, they are still vulnerable to human error, coding bugs, and hacking attacks.
- Impermanent Loss: Impermanent loss is a risk that is specific to liquidity provision in DeFi. Liquidity provision involves users providing liquidity to a decentralized exchange (DEX) or other DeFi application in exchange for a portion of the transaction fees generated by the application. However, if the value of the underlying assets in the liquidity pool changes significantly, users can suffer from impermanent loss, which is a loss of value that occurs when the price of the asset changes relative to another asset in the pool.
- User Error: Finally, DeFi applications are often complex and require a certain level of technical knowledge to use. This means that users who are not familiar with the technology or who make mistakes in their transactions can be at risk of losing their funds. For example, users who enter the wrong wallet address or fail to properly configure their transaction fees can lose their funds or have their transactions fail.
Conclusion
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging trend in the world of finance that has the potential to revolutionize the traditional financial system. DeFi is a decentralized network of financial applications built on a blockchain that operates without intermediaries, such as banks or other financial institutions. DeFi offers several potential benefits over the traditional financial system, including greater efficiency, transparency, and accessibility. However, it also comes with some risks, including a lack of regulation and oversight, market volatility, and smart contract vulnerabilities. As DeFi continues to evolve and mature, it
Popular articles

Jun 08, 2023 07:51 AM

Jun 08, 2023 08:05 AM
Jun 08, 2023 03:04 AM
Jun 07, 2023 04:32 AM
Jun 05, 2023 06:41 AM
Comments (0)